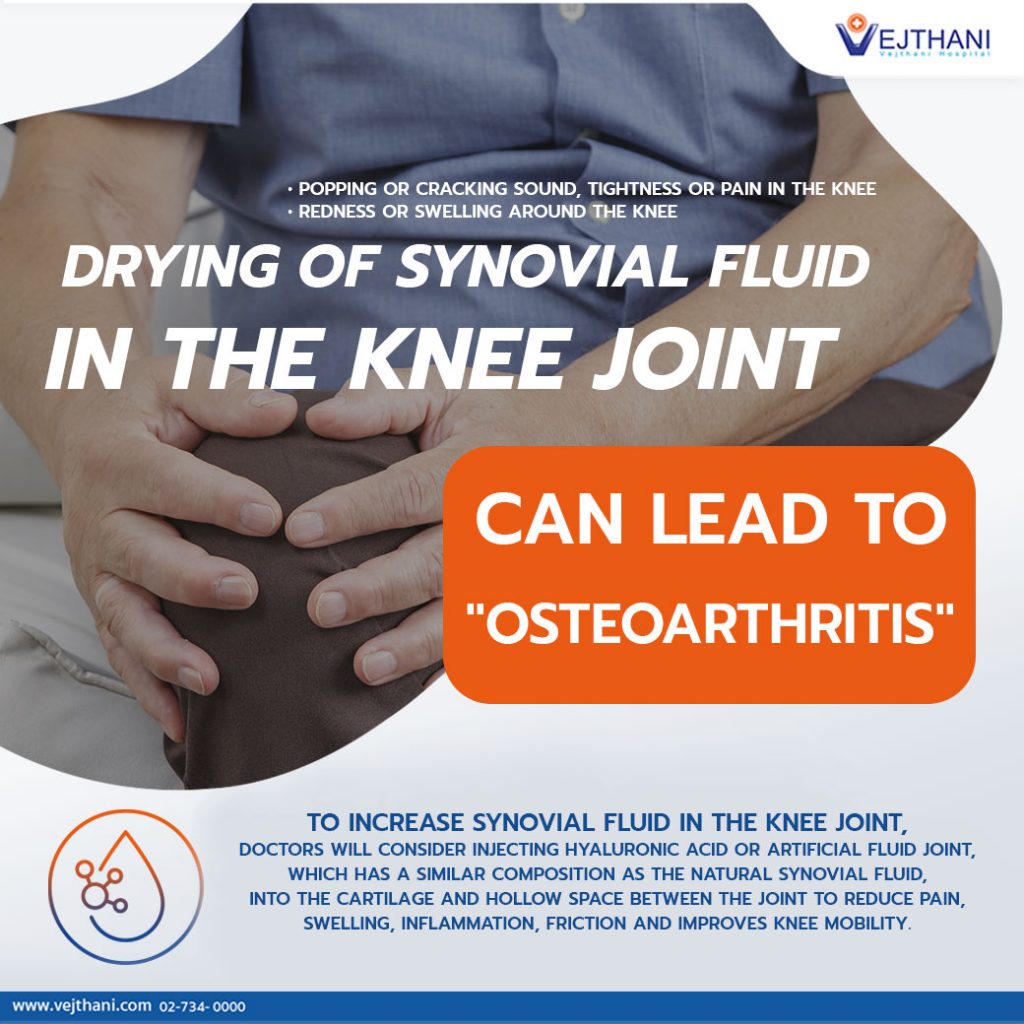

Popping or cracking sound, tightness or pain in the knee could be signs of the decreased synovial fluid. If left untreated, it may lead to knee osteoarthritis.
Synovial fluid or generally known as joint fluid has thick and sticky consistency, act as a lubricant in the knee joint to reduce frictions and as a shock absorber, which helps the movement of our body. Getting up, sitting, or standing could be done effortlessly. Synovial fluid also reduces the pressure on the knee joint as it cushions the ends of bone surface while walking or running.
Naturally our body produces synovial fluid on its own. As we age, our body starts to deteriorate and the amount of joint fluid in the knee decreases. There are also other factors that cause the fluid to dry up quickly. Whether it being overweight, a knee injury or trauma that have severely affected the efficiency of fluid production in the knee joint or wrong physical movement of the knees, like side sitting or bending knees regularly. Certain chronic diseases like diabetes, high blood pressure, or arthritis such as gout or rheumatism are also some of the factors to cause the drying of synovial fluid.
Dr. Premstien Sirithanapipat, Orthopedic surgeon specializing in knee and hip replacement surgery at Vejthani Hospital, reveals that dried synovial fluid can result in knee pain and stiffness. Degeneration of knee joint or injury has symptoms like loud noise in the kneecap especially when walking or bending, swollen or redness surrounding the knee surface. If not treated early, it could potentially lead to osteoarthritis.
“Aside from using medication, to increase synovial fluid in the knee joint, doctors will consider injecting Hyaluronic Acid or artificial fluid joint, which has a similar composition as the natural synovial fluid, into the cartilage and hollow space between the joint to reduce pain, swelling, inflammation, friction and improves knee mobility. The results could be effective for approximately 6-12 months. In addition to the artificial synovial fluid, another treatment option is platelet-rich plasma or PRP injection to repair damaged tissues, treat injury and reduce inflammation. This treatment uses patient’s own blood and undergo multiple processes for a condensed consistency and inject it back to the knee joint. Each treatment option varies upon patient’s condition and doctor’s evaluations”, said Dr. Premstien.
Diagnosis for dried synovial fluid condition, includes history taking, and examination of physical deformation of the knee. Doctor will perform Ballottement test to detect the fluid pressure in the knee joint and look for Balloon Sign to see the pressure of water ripple on the surface of the knee, check for the strength or stability, internal friction or crepitation as well as performing x-ray to examine the damage of the joint. Each diagnostic test depends upon the doctor’s assessment. For those patients who have dried synovial fluid and have not sought medical advice, as a result left untreated, until it reaches to a severe stage of knee osteoarthritis. The treatment options above may not be as effective as they should be and the doctor might have to consider surgical treatment.
For more information, please contact
Hip and Knee Center, Vejthani Hospital
Call: (+66)2-734-0000 Ext. 2222
English Hotline: (+66)85-223-8888
- Readers Rating
- Rated 3.6 stars
3.6 / 5 ( Reviewers) - Very Good
- Your Rating