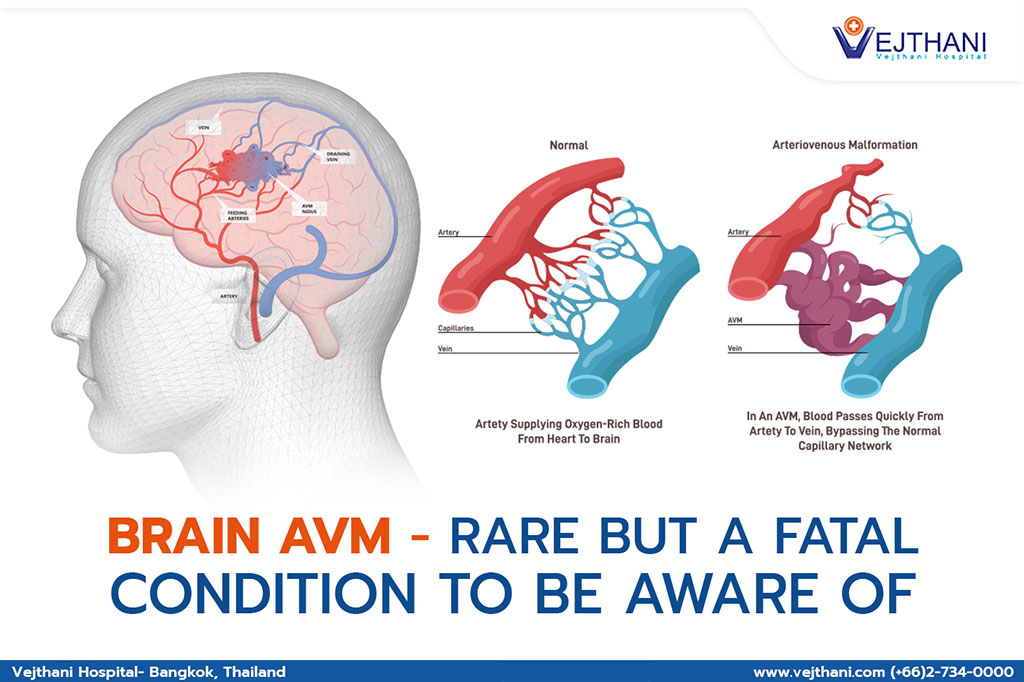

Severe headache, seizures, or pain in one area of the head, or vision loss, difficulty speaking, or severe unsteadiness could indicate a critical medical condition like Brain AVM or arteriovenous malformation. When blood vessels that are connected to the arteries and veins in the brain get tangled with each other, arteriovenous malformation occurs.
The arteries have the responsibilities to carry blood that are rich in oxygen from the heart and supply them to the brain, while veins take the blood that have supplied oxygen back to the lungs and heart. When brain AVM occurs, this crucial process is interrupted.
Most of the patients that have been found with Brain AVM were born with the disease but it can also form later throughout their lives. In rare occasions, it may pass down to the families.
What causes brain AVM is still unknown. Majority of the researchers have found the disease to exist since birth and may form during the fetus development.
Brain AVM does not tend to show any signs and symptoms until the arteries rupture, resulting in hemorrhage. In half of the cases that have been diagnosed with AVM, had hemorrhage as the first sign. Aside from bleeding, other symptoms some patients may experience are:
- Seizures
- Headache in one part of the head
- Weakness or numbness in muscles in one part of the body or paralysis
- Loss of vision
- Difficulty speaking
- Confusion or inability to understand other people
- Severe unsteadiness
As AVM puts heavy pressure on the walls of the arteries and veins that are affected, they become weak and results in AVM rupture or bleeding in the brain. The disease can also cause complications from the reduction of oxygen in the brain tissue or having brain damage.
If patient is suspected of having a brain AVM, a CT scan or an MRI is used to diagnose the disease. Cerebral angiography is also used as it is the most detailed diagnostic test that disclose the location and characteristics of the affected arteries and veins which are crucial information in planning the treatment.
A several treatment options are available for brain AVM with the primary objective of the treatment is to inhibit the occurrence of hemorrhage. To control seizures or other neurological conditions are also taken into account when treating the patient. The most appropriate treatment option varies on the age and health of the patient, and the size and location of the AVM. Surgery or resection to remove the AVM would be the most common treatment when there is a minor risk for the patient to have a brain hemorrhage or seizures. The procedure is done by the use of high powered-microscope to seal off the AVM and remove it from the nearby tissue with medical clips. Endovascular embolization and Stereotactic radiosurgery are other options to treat the disease.
It is extremely crucial to seek medical attention as soon as any signs of brain AVM show through. If bleeding occurs in the brain, AVM becomes life-threatening and needs immediate medical attention.
In case of having suspected symptoms of brain AVM, doctor may recommend a brain MRI to screen the condition of the patient. MRI is a medical investigation that uses strong magnets and radio waves to produce clear images of the brain. It is more detailed than CT scan as it displays even the tiniest changes in the brain tissue that are linked to brain AVM. It indicates precise locations of the brain AVM and the internal bleeding spots, which is vital information that helps doctors to evaluate the condition so accurate treatment options can be provided. This makes MRI an effective screening test to rule out brain AVM or other neurological conditions.
For more information, please contact
Neuroscience Center, Vejthani Hospital
Call: (+66)2-734-0000 Ext. 5400
English Hotline: (+66)85-223-8888
- Readers Rating
- Rated 4.5 stars
4.5 / 5 ( Reviewers) - Outstanding
- Your Rating