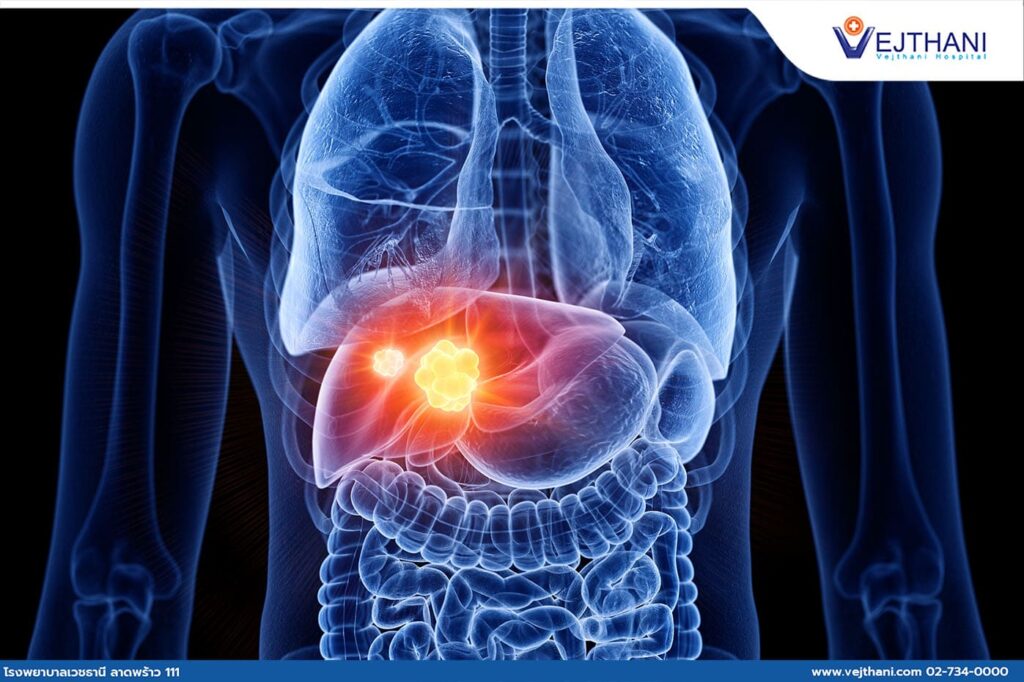

Liver cancer is the most prevalent type of cancer in Thailand. Most liver cancer patients seek medical advice when the disease has already worsened and is in the final stage. In most cases, the detected malignant tumor is often too large to be surgically removed. Currently, a more promising treatment for liver cancer known as Transarterial Chemoembolisation (TACE) is available.
Clear causes of liver cancer are still unknown. However, the disease is primarily associated with any of these factors:
- Hepatitis B and/or C virus infection: Chronic infection may eventually develop into liver cancer if left untreated.
- Liver cirrhosis: Patients with liver cirrhosis tend to have a higher chance of developing liver cancer than normal people by 270 times.
- Chronic alcoholism: Consuming over 80 grams of alcohol per day continuously for five years poses the risk of developing liver cancer by 8–12 times.
- Liver flukes: A liver fluke is a parasite found in freshwater fish and raw or semi-cooked food.
- Consuming food that is high in aflatoxin, such as peanuts, corn, chili, onion, garlic, and bean paste, as well as food high in nitrosamine, including pickled fish, Chinese sausage, salt-cured meat, salted fish, and dried shrimp.
- Obesity: Obesity, especially abdominal obesity, raises the risk of fatty liver.
The best treatment among various methods is to remove the tumor surgically. However, most patients have limitations that make surgery impossible, such as old age, liver cirrhosis, or tumors in multiple locations. Hence, Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) has become increasingly popular. The procedure is done by administrating chemotherapy directly through the artery to treat the cancerous tumor in the liver.
TACE delivers chemotherapy precisely to specific areas in the body. A catheter is inserted into an artery in the groin and threaded up to the liver. Then, the chemotherapy drug is injected directly into the blood vessels that feed the tumor and block the blood vessels with gel foam made of small gelatin to prevent blood from flowing back to the cancerous tumor. This will eventually cause the tumor to shrink and die.
The amount of chemotherapy administered is low compared to intravenous chemotherapy. Therefore, side effects of chemotherapy in other parts of the body are reduced.
Nevertheless, some remaining cancer cells may reaccumulate themselves by stimulating the surrounding healthy cells to build new blood vessels to supply blood to the tumor. Hence, TACE may need to be done every 4-6 weeks. If the tumor is large or present in multiple areas, Transarterial Chemoembolization can be done to eliminate the remaining cancer cells.
- Readers Rating
- Rated 3.9 stars
3.9 / 5 ( Reviewers) - Excellent
- Your Rating