Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Early-Stage Alzheimer’s: Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Learn about Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and early Alzheimer’s. Discover diagnosis and IV infusion therapy that may slow disease progression.
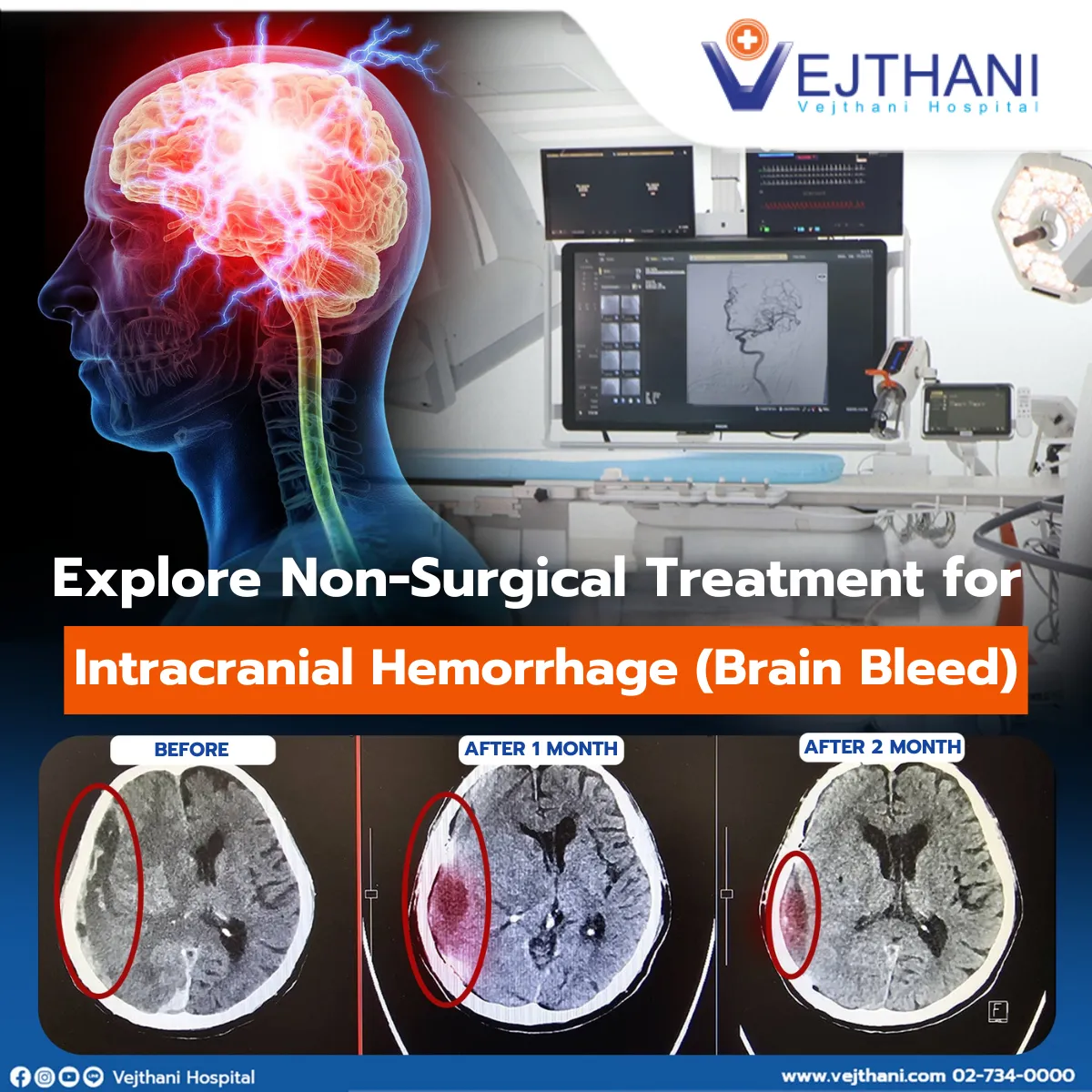
Accidents can happen to anyone, anywhere, but older adults need to be especially cautious about even minor head impacts, as these can lead to intracranial hemorrhage, which is characterized by bleeding within the brain. The condition may become life-threatening.
Dr. Pongsakorn Pongsapas, neurosurgeon at Vejthani Hospital, explained that repeated head impacts, whether from car accidents, falls, collisions with hard objects, or sports-related injuries, can lead to severe brain injuries. This is especially concerning for older adults, as head injuries can more easily result in intracranial hemorrhage. As older people age, their blood vessels become fragile, making them more susceptible to bleeding compared to younger people.
In the initial stage, some patients with intracranial hemorrhage may show no symptoms. However, as time passes, the bleeding may increase and accumulate, resulting in a chronic hematoma that compresses brain tissue. Symptoms, such as headaches and weakness, usually appear after about a month. If left untreated, complications can arise, including cognitive decline, paralysis, or even death.
The conventional approach for treating intracranial hemorrhage involves open brain surgery to remove accumulated blood, reducing brain pressure and preventing further brain damage. This approach requires a lengthy recovery period.
However, advancements in technology can help treat intracranial hemorrhage with a non-surgical method. Catheter insertion and Endovascular Embolization are done to stop brain bleeding.The procedure is done by a neurosurgeon specializing in interventional radiology. It involves numbing the groin area and inserting a thin catheter into a blood vessel through the groin. The catheter is guided to the damaged area in the brain. Once it reaches the bleeding site, the surgeon will inject an adhesive or special polymer, like cyanoacrylate glue, into the vessel. This seals the vessel or the leak, stopping the bleeding at its source.
This procedure not only prevents the need for surgery but also eliminates the requirement for general anesthesia, reducing the risk of complications and infection. Moreover, the recovery time is reduced, often requiring just a one-night hospital stay.
“After treating intracranial hemorrhage, patients may still experience headaches and weakness for about 2-4 weeks, with gradual improvement. However, they need continuous self-care to avoid further injury,” said Dr. Pongsakorn Pongsapas.
Frequent head injuries that lead to brain hemorrhages require prompt medical attention and specialized care. With state-of-the-art medical technology and surgical techniques, patients can now recover swiftly and regain a high quality of life. The collaborative effort between doctors and patients, including personalized treatment plans and rehabilitation, plays a vital role in ensuring a smooth and speedy recovery.
Neuroscience Center, Vejthani Hospital
Call: (+66)2-734-0000 Ext. 5400
English Hotline: (+66)85-223-8888
