How is Esophagogastroduodenoscopy Used in Diagnosis?
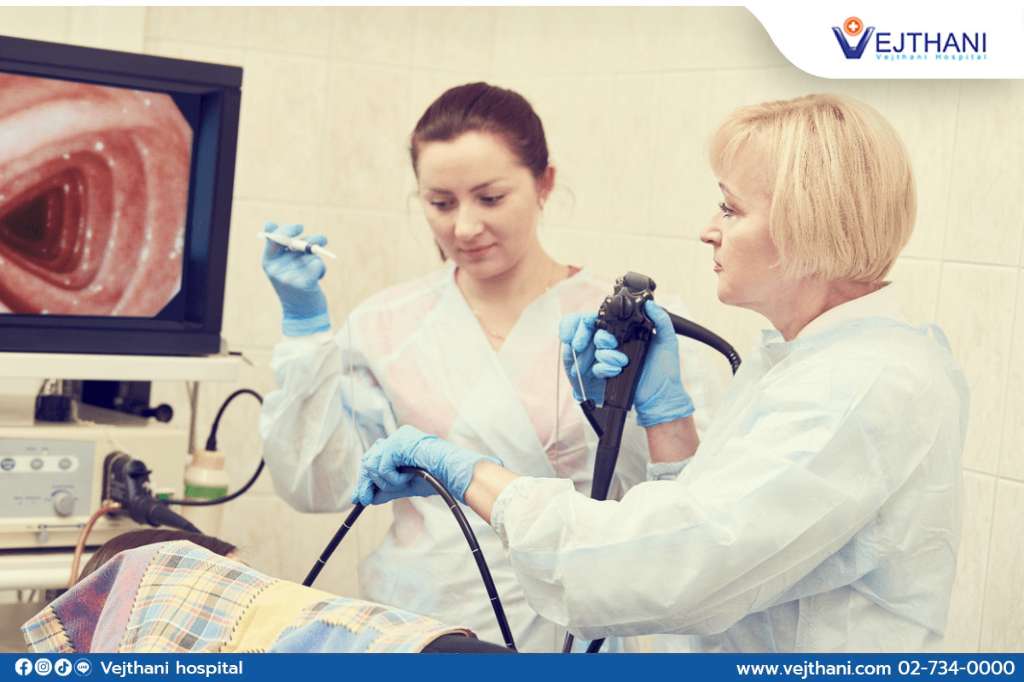
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), is a diagnostic process that uses an endoscope to probe the gastric, duodenal and intestinal areas of the body.
The endoscopes of today are a far cry from the bulky and cumbersome endoscopes of the past. The first widely-used endoscopes used fiber-optics to provide light and transmit an image of the interior cavities of the body to a lens doctors could look through to determine their diagnoses of the patient’s problem.
Modern endoscopes are much thinner and cause much less discomfort to the patient, as well as being much more comfortable for a doctor to use. Today’s endoscopes usually make use of a tiny camera mounted on the end of the tube to send a video image to a monitor.
In both the early and modern versions, the scopes are highly flexible, and the tip can be controlled remotely by the doctor performing the esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
Procedure of Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
A patient about to undergo an EGD process will have their vital signs monitored throughout the procedure. Medicine will be injected into the patient to help them relax. A local anesthetic is sprayed into the mouth and throat to lessen the patient’s gag reflex, and a mouth guard is used as well to protect both the patient’s teeth and the endoscope from any damage.
Any dentures are removed from the mouth to facilitate the insertion of the scope, and the patient will be instructed to lie on their left side during the procedure.
In the event of a narrowed or constricted esophagus, treatments can be performed that will rectify the problem.
The scope is inserted through the esophagus and down into the stomach and duodenum. Air is usually pumped into the cavities as well to prevent the stomach walls from obscuring the image from the endoscope.
The esophagus is examined as the scope is inserted. The stomach lining and top of the duodenum is examined once the scope reaches those areas. Tissue samples can be collected, and biopsies can be performed by using the endoscope.
Uses of Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
EGD can be used to diagnose and evaluate a number of gastric and digestive problems. It’s a relatively quick and painless diagnostic tool that can help doctors verify the cause behind symptoms such as abdominal pain, trouble swallowing, heartburn and gastric reflux, persistent vomiting, and bloody stools.
If a patient has an ongoing gastric or digestive problem, it can also be used as a minimally-invasive procedure for periodic monitoring of the patient’s condition. As the procedure generally can be done in less than an hour, and it’s an out-patient procedure, a patient can have the procedure performed regularly.
EGD is also used to locate and remove foreign objects from the stomach. Surgery to control bleeding can also employ esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
If you have any gastric or digestive problem, make an appointment with the Gastroenterology and Hepatology Center at Vejthani Hospital. Our doctors use the latest diagnostic techniques, including EGD, to diagnose your problem quickly and prescribe effective treatment.
- Readers Rating
- Rated 5 stars
5 / 5 ( Reviewers) - Spectacular
- Your Rating