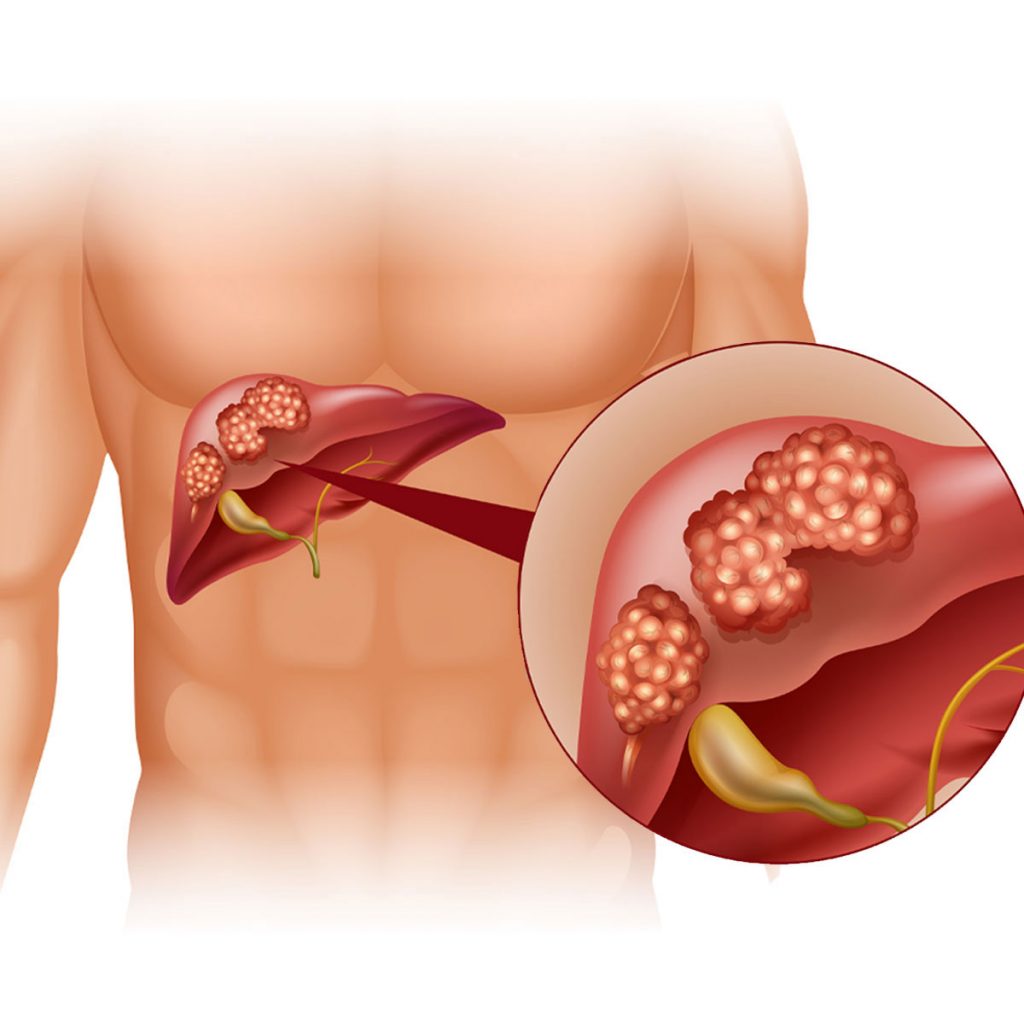
Liver cancer

Overview
The liver is an organ that has a size as big as a football located at the upper right area of the abdomen just above the stomach and below the diaphragm. Liver cancer begins at the liver cells (hepatocytes). The most common type of liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma that mainly affects the hepatocytes. There are other types of liver cancer which are rare such as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatoblastoma.
Cancers that originate from other parts of the body (e.g. breast, lung or colon cancer) can spread to the liver. This is called metastatic cancer.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms mostly not show when primary liver cancer is in its early stage.
The following are the signs and symptoms of liver cancer:
- Unintentional weight loss
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Pain in the upper abdomen
- Swollen abdomen
- Jaundice (yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes)
- Dark-colored urine
- Pale/clay-colored stool
If you have any of these signs and symptoms and it worries you, consult a doctor.
Causes
Liver cancer generally starts from the DNA mutation of the normal cells. The mutation of liver cell causes uncontrolled duplication resulting in forming a mass of cells also known as a liver tumor. This tumor then begins to invade and destroy the healthy tissues.
The cause of liver cancer may be known such as having chronic infection with hepatitis. However, the cause is sometimes unknown if there are no underlying conditions which may have resulted in liver cancer.
Risk factors
These are the factors which may develop into primary liver cancer:
- Chronic infection with Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) or Hepatitis C Virus (HCV).
- Cirrhosis. Cirrhosis causes scars in the liver and can result to liver cancer.
- Inherited liver disease. Hemochromatosis and Wilson’s disease are some of the diseases that can result to liver cancer.
- Having Diabetes.
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Fat accumulation in the liver can increase the risk of liver cancer.
- Exposure to aflatoxins. Aflatoxins are toxic materials that come from molds that can be found on crops (e.g. grains and nuts) that are not stored properly. The toxins may contaminate the food produced by the crops.
- Excessive alcohol consumption. Heavy alcohol use results to liver damage that cannot be reversed and may lead to liver cancer.