
Pertussis, also known as whooping cough or the “100-day cough,” is a respiratory infection caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. It leads to a series of coughing fits followed by a distinctive “whooping” sound as the patient inhales, resembling a “snoring” sound.
This disease significantly affects young children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems. In its early stages (1–2 weeks), symptoms are like the common cold, such as coughing, runny nose, and low-grade fever. In the second stage (2-8 weeks), patients develop intense coughing fits that may lead to breathing difficulties, whooping sounds, and even vomiting after severe coughing episodes.
Pertussis can be treated with appropriate antibiotics, especially when administered early in the disease. High-risk patients, such as young children, may require hospitalization.
Vaccination remains the most effective way to protect against pertussis.
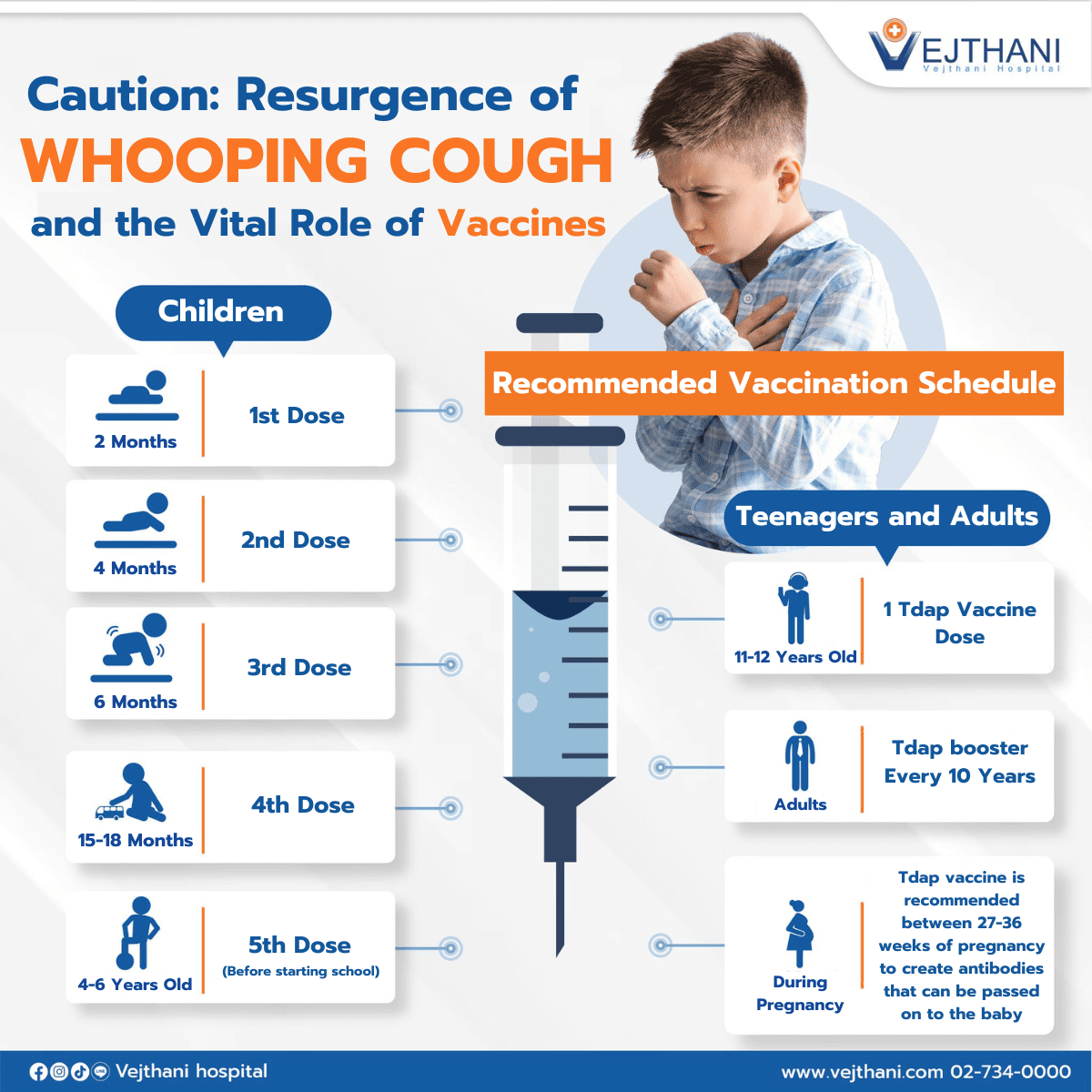
Generally, all children receive their first dose of the Bordetella pertussis vaccine at 2 months of age. However, the immunity provided by the vaccine is not lifelong, and protection decreases over time. This makes adults and older elderly vulnerable to reinfection. Even though adults may not show severe symptoms, they can still transmit the infection to infants and those with weakened immune systems.
Multiple booster vaccinations are necessary to maintain sufficient immunity. Pertussis vaccines are typically administered in combined vaccine DTaP (Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis) or Tdap for children and adults, according to recommended vaccination schedules (as shown in the graphic).
Although pertussis is vaccine-preventable, the current outbreaks emphasize the need for complete and timely vaccination to reduce infection risks and prevent transmission, especially to high-risk groups.
For more information, please contact
Super Kid’s Center, Vejthani Hospital
Call: (+66)2-734-0000 Ext. 3310, 3312, 3319
English Hotline: (+66)85-223-8888
- Readers Rating
- Rated 4.9 stars
4.9 / 5 ( Reviewers) - Spectacular
- Your Rating




























