Some seemingly common symptoms, like severe headaches, seizures, or unexplained headaches in specific areas, could be warning signs of a severe underlying condition. It could be Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM), a cerebrovascular abnormality that can affect the nervous system and may be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Dr. Pongsakorn Pongsapas, a neurosurgeon at Vejthani Hospital, explained that Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM), occurs when blood vessels connecting arteries and veins in the brain become tangled. Arteries are responsible for carrying oxygen-rich blood from the heart to nourish the brain, while veins carry oxygen-depleted blood from all parts of the body back to the heart. When AVM occurs, blood cannot flow normally. If the abnormal blood vessels exert strong pressure on the walls of the arteries and veins, these vessels can become fragile and prone to rupture, potentially leading to a brain hemorrhage.
Several studies have found that Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) can be present from birth and may develop during fetal development. AVM is commonly found in patients with Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT), also known as Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome. This condition typically affects blood vessel formation in various parts of the body, including the brain. However, the exact cause of AVM remains unclear.
AMV is more common in men than women, and there is an increased risk if there is a family history of this disease. Symptoms usually appear gradually between the ages of 10 and 40, becoming more noticeable in adulthood, or maybe no symptoms until a blood vessel ruptures, causing a brain hemorrhage. For some patients, symptoms only begin after a brain hemorrhage has occurred. Associated symptoms that may occur include:
- Seizures
- Headache in a specific area of the head
- Muscle weakness or numbness in a particular area of the body or paralysis
- Loss of vision
- Slurred speech
- Confusion, dizziness, or inability to communicate with others
- Complete loss of balance and movement
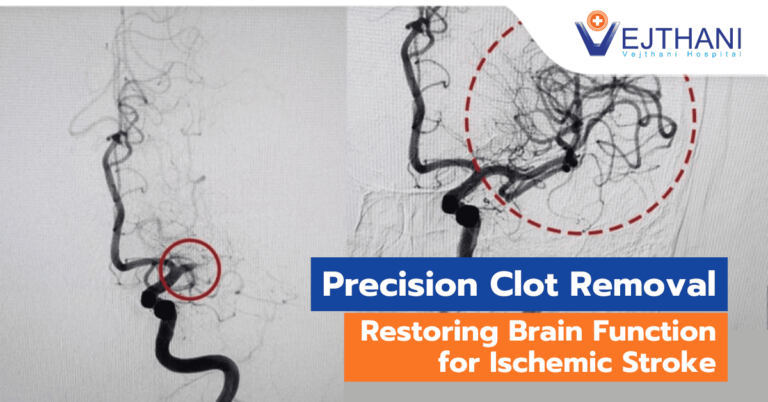
Diagnosis of AVM can be done through various methods, depending on the doctor’s discretion. One of the most precise diagnostic tests is Cerebral Angiography, which offers the highest resolution and is highly effective in identifying the location and characteristics of the affected arteries and veins. Other diagnostic methods include CT scan and MRI.
An MRI scan can pinpoint the location of AVM and provide detailed images of changes in brain tissue without causing pain, as it does not require the insertion of any catheters into blood vessels, and the patient is not exposed to radiation.
There are several treatment options for AVM, and the doctor will choose the most appropriate method based on the patient’s age and overall health. The primary objective is to prevent brain hemorrhage. Surgical removal of the abnormal blood vessels may be the best option for patients with a low risk of bleeding or seizures. In such cases, doctors may perform endoscopic surgery. Other treatment methods include Endovascular Embolization and Stereotactic Radiosurgery.
If you experience symptoms that may indicate AVM or have a brain hemorrhage, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible to receive timely treatment, as this could be life-threatening.
For more information, please contact
Neuroscience Center, Vejthani Hospital
Call: (+66)2-734-0000 ext. 5400
English Hotline: (+66)85-223-8888
- Readers Rating
- Rated 4.8 stars
4.8 / 5 ( Reviewers) - Spectacular
- Your Rating