
Cerebral aneurysms or brain aneurysm don’t tend to show symptoms until they become severe. The disease progresses to an advanced level by the time it is detected. If not treated properly in time, it can lead to paresis, paralysis, or even death.
Dr. Pongsakorn Pongsapas, a neurosurgeon at Vejthani Hospital, stated that a cerebral aneurysm is an abnormality of a weak blood vessel in the brain. It causes a bulging blood vessel that resembles a balloon and can easily rupture. It can occur in anyone but is more common in individuals over 40. Risk factors include certain genetic disorders, a family history of cerebral aneurysm, untreated hypertension, smoking, and older age.
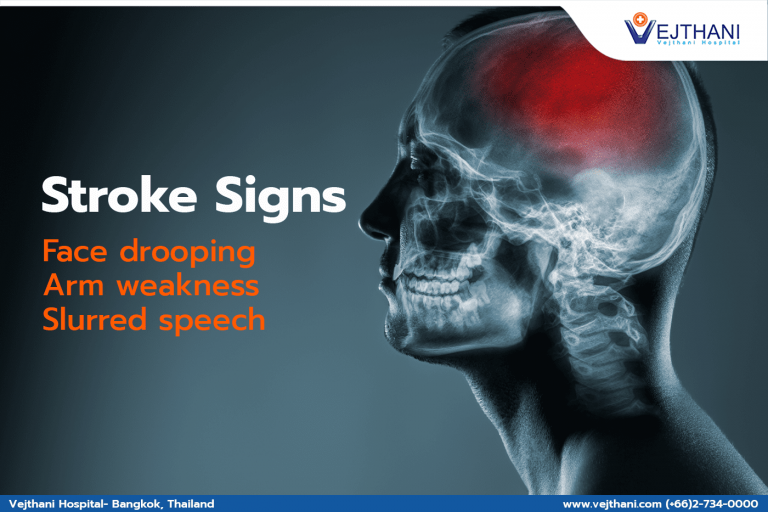
The symptoms of brain aneurysm do not tend to appear when it starts to develop. The following symptoms may occur after the vessel ruptures or bulges press against the brain tissue or nerves.
- Severe headache
- Vomiting
- Double vision
- Stiff neck
- Blurred vision
- Seizure
- Drooping eyelid
- Loss of consciousness
- Facial Palsy
- Numbness of one side of the body
- Trouble speaking
- Dysphagia
People with cerebral aneurysms are usually unaware of the symptoms until they have a severe headache. A health checkup is a great way to detect cerebral aneurysms. The disease can be diagnosed by CT scan and MRI, which detect any abnormal blood vessels in the brain. Cerebral Angiography is used to detect the current situation, size, and location of the cerebral aneurysm with more detailed images.
There are several methods to treat cerebral aneurysms.
- Stent Implantation: inserting a stent into the bulging blood vessel.
- Microsurgical clipping: An operation that opens the skull and blocks the blood flow to the bulging blood vessel to stop the rupture.
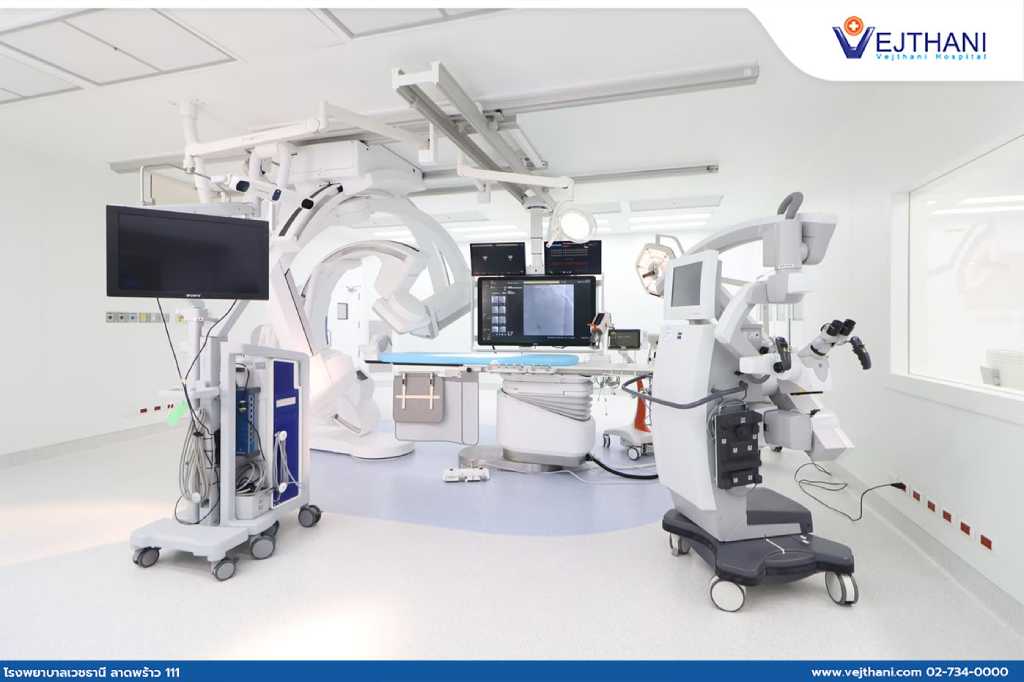
- Biplane DSA (Biplane Digital Subtraction Angiography) is currently the most preferred treatment for cerebral aneurysms. The method uses special types of X-ray machines that can capture images of blood vessels in two planes simultaneously, retrieving more precise visualization of the position and shape of the blood vessels. During the procedure, equipment as tiny as the tip of a pen is inserted into the groin area, along with the insertion of small catheters into blood vessels in the brain. Then, a contrast dye is injected while the Biplane DSA machine is rotating to create clear images and calculate the size of the coils needed for treatment. This makes the treatment safer and faster than conventional CT injectors.
Biplane Digital Subtraction Angiography is an advanced technology that requires less radiation exposure than traditional treatment methods. It has a quicker duration and leaves no scars or minimal scars resembling a tiny wound in the groin area. This approach reduces complications and enhances fast recovery.
For more information, contact
Neuroscience Center, Vejthani Hospital
Call 02-7340000 or Ext. 5400
English Hotline: (+66)8-522 3888
- Readers Rating
- Rated 5 stars
5 / 5 ( Reviewers) - Spectacular
- Your Rating