Overview
Acute kidney failure is a medical condition in which the kidney suddenly decreases in the ability to excrete waste product, balance fluid and electrolyte in the body. If the kidneys are not functioning well, the waste products build up in the body and cause the blood’s chemical component to be out of its normal range.
Acute kidney failure, which is often referred to as acute renal failure or acute kidney injury, occurs suddenly, typically within a few days. Patient who needs intensive care due to serious medical condition tend to have higher risk of developing acute kidney failure.
Acute kidney injury can be very serious and needs aggressive management. However, it is not always permanent and may still be curable. It is possible to regain normal or almost normal kidney function if you are treated early.
Symptoms
The common symptoms of acute kidney failure vary in every individual. Common signs that you may notice includes:
- Fluid retention that causes swelling of the extremities
- Shortness of breath or difficulty in breathing
- Fatigues or weakness
- Decreased urine output
- Irregular heartbeat or arrhythmia
- Chest pain
- Confusion
- Seizures
- Nausea and vomiting
In some cases, no noticeable signs or symptoms may occur. It is usually discovered by doctors in laboratory results requested from the patient for a different purpose.
It is advised to seek the doctor immediately if the patient noticed any of the signs or symptoms.
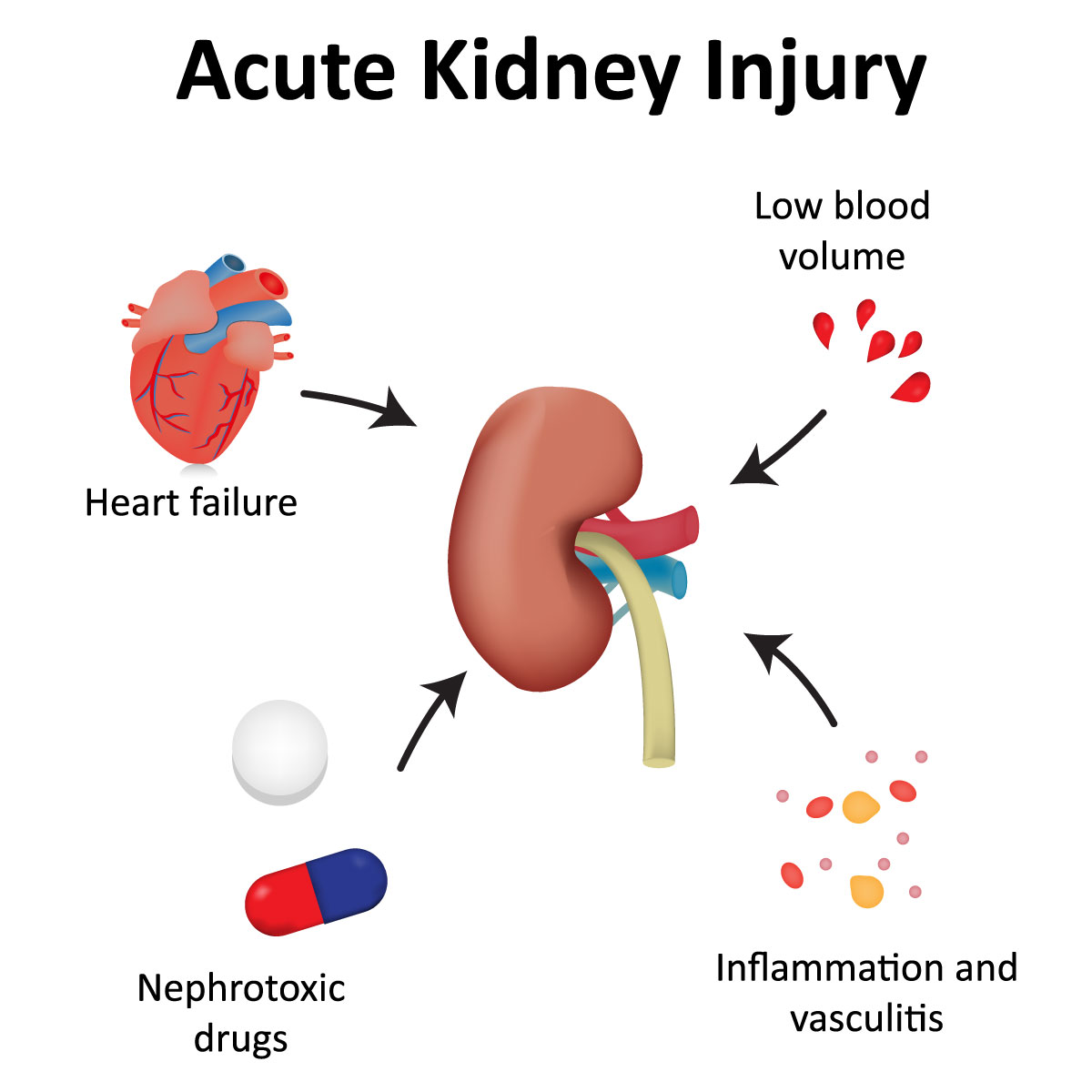
Causes
Acute kidney failure is often associated with:
- A condition that disrupts blood flow to the kidneys
- Direct damage to your kidneys
- Obstruction on urine drainage tubes (ureters) which prevents wastes to leave the body through your urine
Impaired blood flow to the kidneys
There are several illnesses and disorders that can reduce the amount of blood that enters the kidneys, resulting in kidney damage. These includes:
- Heart disease or heart attack
- Liver failure
- Fluid loss or severe dehydration
- Extreme blood loss
- Medications such as aspirin, pain medication, or blood pressure medication.
- Allergic reaction
- Burns
Damage to the kidneys
These illnesses, conditions and substances may harm the kidney and cause acute renal failure:
- Blood clots in and around kidney’s veins and arteries
- Cholesterol buildup in the kidney that obstructs blood flow
- Glomerulonephritis is an inflammation to the glomeruli or tiny filters inside the kidneys
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome, a disorder that happens when the red blood cells are destroyed
- Infection, like from the virus that cause COVID-19 disease
- Lupus, is an autoimmune disease that causes glomerulonephritis
- Medications including certain chemotherapy drugs, antibiotics, and imaging test dyes
- Scleroderma, an uncommon condition that involves the skin, internal organs, and connective tissues
- Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, a rare blood disease
- Toxins like cocaine, heavy metals, and alcohol
- Kidney injury brought on by toxins produced by the breakdown of muscular tissue (rhabdomyolysis)
- Tumor lysis syndrome, caused by the disintegration of tumor cells, results in the release of toxins that can harm the kidneys
Urine blockage in the kidneys
Several illnesses and disorders that causes urinary blockages and can result in an acute kidney injury:
- Blood clots in the urinary tract
- Bladder cancer
- Cervical cancer
- Colon cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Enlarged prostate
- Kidney stones
- Nerve damage responsible for bladder control
Risk factors
Acute kidney failure usually cause by a result of a complication from other serious medical condition. There are several factors that increases the risk of acute kidney failure. These includes:
- Hospitalized due to serious illness that needs intensive treatment
- Advanced age
- Peripheral artery disease, obstruction in the blood vessels that restricts blood flow in the arms or legs
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Heart failure
- Kidney diseases
- Liver diseases
- Certain cancers and their treatments
Diagnosis
The medical professional may advise specific tests and procedures to confirm the diagnosis if the patient are already experiencing signs and symptoms of acute renal failure. These may consist of:
- Urine output measurements: The medical professional may be able to identify the reason of the kidney failure by measuring how much the patient urinate in a 24-hour period.
- Urine tests: Urinalysis, a procedure in which the urine sample is examined to discover possible abnormalities related to kidney disease.
- Blood tests: The blood sample may show accelerating levels of urea and creatinine, two markers of renal function. Rising levels of these substances means that the kidneys are not functioning effectively.
- Imaging tests: The medical professional may use imaging tests like ultrasound and computerized tomography (CT) scan to provide them with a better visual image on the health of the kidneys.
- Kidney biopsy: Medical professional may occasionally advise a kidney biopsy to take a tiny sample of kidney tissue for laboratory analysis. To take the sample, doctor uses a needle to penetrate the skin and enter the kidney. This procedure is recommended if the cause of kidney failure is difficult to determine.
Treatment
Treatment for acute kidney failure usually involves inpatient care or hospitalization. The cause of the acute renal failure and the speed at which the kidneys recover will determine the length of stay in the hospital.
In some cases, recovery can be done at home. Medical professional will orient the patient and the family with the necessary support care while on home recovery.
Treating the cause of the kidney injury
Treatment for acute kidney failure requires determining the illness that initially caused the kidney damage. The cause of the renal failure also determines the kind of treatment that you must undergo.
Treating complications
For a continuous recovery, medical professional will regularly monitor you to prevent any complications. The kidneys should heal at its own pace. Several treatments are also necessary to support its recovery, this includes:
- Treatments to balance the amount of fluids in the blood: medical professional could advise intravenous (IV) fluids if the acute kidney failure is brought on by a deficiency of fluid in the blood. In some instances, acute renal failure might result in having too much fluid, which will cause the arms and legs to bulge. Medical professional may prescribe drugs (diuretics) in certain circumstances to encourage the body to flush out extra fluids.
- Treatments to control blood potassium: Medical professional may advise calcium, glucose, or sodium polystyrene sulfonate to avoid the buildup of high levels of potassium in the blood if the kidneys are not effectively filtering potassium. Muscle weakness and arrhythmias can both result from an excess of potassium in the blood.
- Treatments to restore blood calcium levels: Medical professional might advise a calcium infusion if the calcium levels in the blood become too low.
- Dialysis to remove toxins from your blood: If toxins accumulate in the blood, they could require short-term hemodialysis, often known as dialysis, to assist the body get rid of toxins and extra fluids while the kidneys recover. The body may be able to lose extra potassium with the aid of dialysis. A machine that filters waste product through an artificial kidney (dialyzer) which will pump blood out of the body during dialysis. Then the body receives the blood back. Basically, this treatment does what the kidneys can no longer do.




