Brain Aneurysm Treatment

Overview
Brain aneurysm is a potentially life-threatening condition that demands immediate care and treatment. Vejthani Hospital provides expert treatment of brain aneurysms in Thailand.
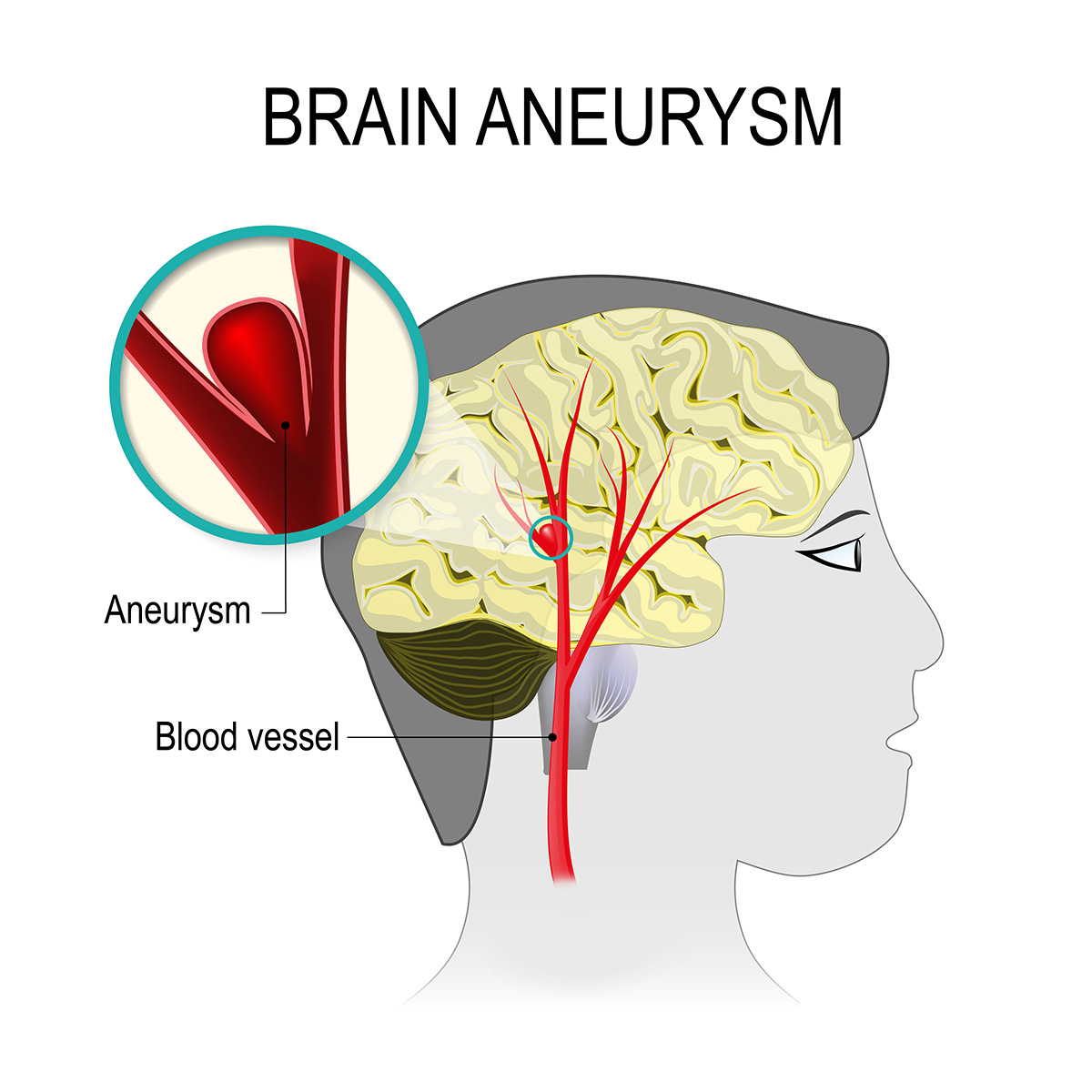
Brain aneurysms, also known as cerebral aneurysms, is a bulge or ballooning in a blood vessel in the brain, filled with blood. Brain aneurysms develop as a result of thinning artery walls. Because those areas of the vessels are weaker, aneurysms frequently form at forks or branches in arteries.
Brain aneurysms show no symptoms until they rupture or leak, causing bleeding in the brain, known as a hemorrhagic stroke. Hemorrhagic stroke could lead to brain damage and is life-threatening. A ruptured brain aneurysm typically develops between the brain and the delicate tissues that cover the brain; this is called subarachnoid hemorrhage.
However, there are brain aneurysms that do not rupture or create any symptoms or problems. Aneurysms are commonly found during examinations for other disorders. A variety of techniques are used as treatments for ruptured aneurysm, aim to block blood from entering into the aneurysm and to divert blood flow across the aneurysm to prevent rupture.
Symptoms
- Ruptured aneurysm: The primary sign of an aneurysm rupture is an abrupt, severe headache. The following are typical warning signs and symptoms of an aneurysm rupture in addition to a severe headache:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Blurred vision
- Sensitive to light
- Stiff neck
- Confusion
- Seizure
- Loss of consciousness
- Leak aneurysm: An aneurysm may occasionally leak small amount of blood which will result in an abrupt, excruciating headache. Leaking is frequently followed by a more serious rupture.
- Unruptured aneurysm: There could be no symptoms if a brain aneurysm does not rupture. However, a larger, unruptured aneurysm could put pressure on the brain’s tissues and nerves that, potentially will lead to:
- Facial numbness on one side
- Pain above and behind one eye
- Dilatation of pupil
- Vision change or double vision
Seek immediate medical attention if you are with someone who has a sudden, severe headache, loses consciousness, or has a seizure.
Cause
The causes of brain aneurysms are still unknown, or the causes of leakage or rupture, but anything that increases your blood pressure can be dangerous. Higher blood pressure makes blood push harder against blood vessel walls, which may increase the risk.
Risk factors
The likelihood of a brain aneurysm or an aneurysm rupture can increase because of artery wall weakness caused by the following:
- Age: Adults are more prone to brain aneurysms than children.
- Gender: It affects women more frequently than men.
- Family history: Family members such as parents, siblings, or children that have a history of brain aneurysms.
- Genetic disorders: such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Marfan syndrome, neurofibromatosis type 1, or Loeys-Dietz syndrome, are connective tissue genetic disorders.
- Other diseases: Having an uncommon blood vessel condition such as cerebral arteritis, fibromuscular dysplasia, or arterial dissection. Also, people suffering from polycystic kidney disease.
If you are within one of the high-risk categories for aneurysms, consult with a doctor at Vejthani Hospital to discuss preventive measures and treatment options to reduce your risk.
Contact Information
service@vejthani.com