Overview
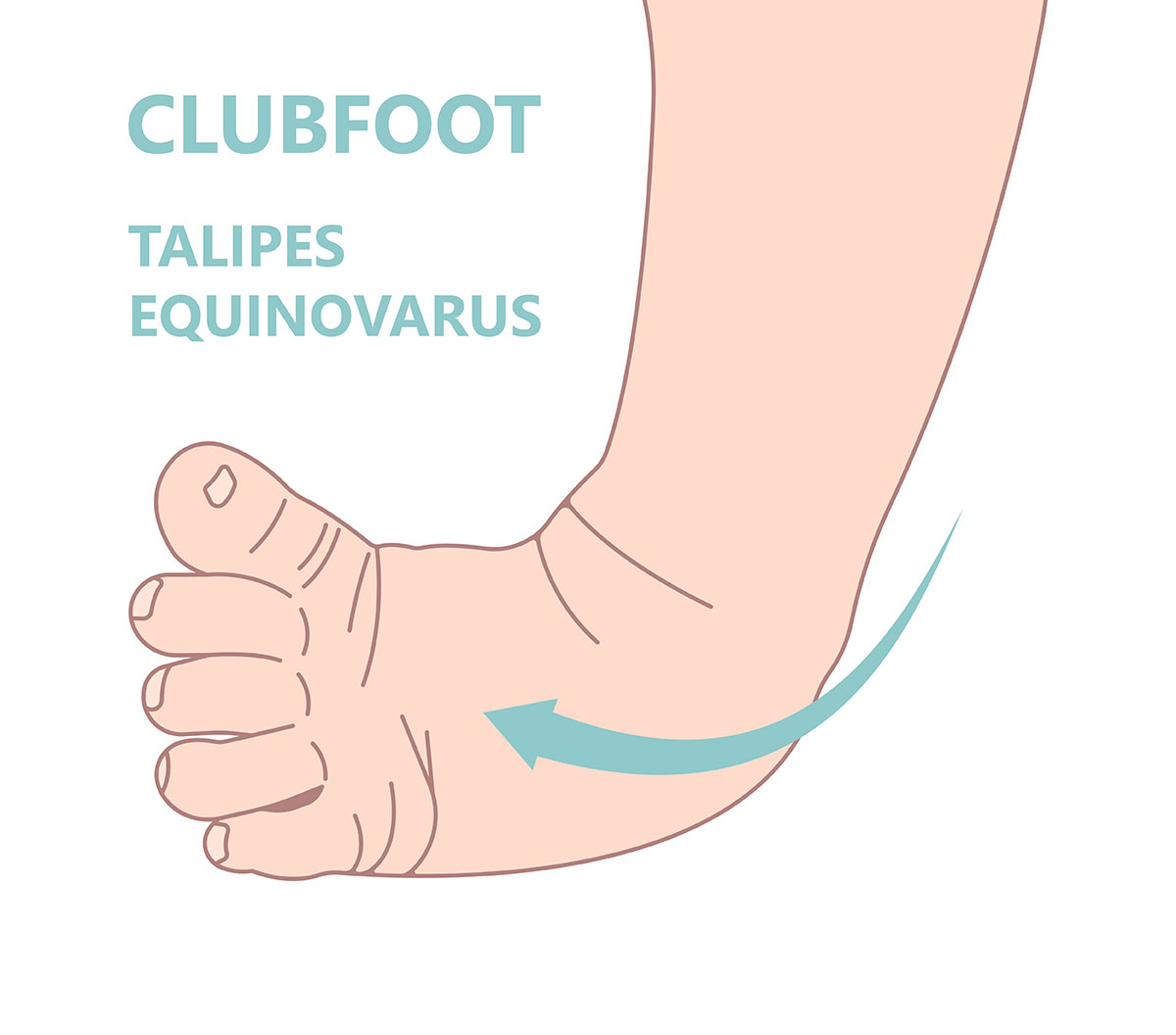
Clubfoot is a variety of abnormalities of the foot which is mostly congenital. In clubfoot, the Achilles tendon is too short and the bones of the foot and ankle are misaligned due to differences in the muscles and tendons acting on the foot, causing the baby’s foot to twisting out of position or shape.
Types of clubfoot
- Idiopathic Clubfoot. Most common and usually present at birth. Idiopathic Clubfoot is also called talipes equinovarus. One out of 1,000 newborns can have this condition and more common in boys. Half of them have this condition in one foot.
- Neurogenic Clubfoot. This clubfoot develops due to neurologic condition such as having spina bifida. The clubfoot can also develop later as the baby grows a little older due to spinal cord compression or cerebral palsy.
- Syndromic Clubfoot. A clubfoot which exists together with other clinical conditions caused by a syndrome such as constriction band syndrome, tibial hemimelia, diastrophic dwarfism, and arthrogryposis.
Clubfoot can be mild or severe and occurs in one or both feet which results to difficulty in walking. Doctors recommend that it should be treated as soon as possible.
Signs and symptoms
Clubfoot has the following signs and symptoms:
- The foot turns inward and downward with toe pointing toward the opposite foot
- Clubfoot may be twisted upside down in severe cases
- The leg on the affected side is often shorter than on the other side.
- Smaller calf muscle on the leg with clubfoot
If you notice any of these symptoms, seeing a pediatric orthopedist is recommended.
Risk factors
- Gender.Males generally has a greater chance of acquiring clubfoot.
- Family history. If any of the family members had a clubfoot, the child is most likely to inherit the same condition.
- Congenital conditions. Other congenital conditions related to underdeveloped spine (e. Spina bifida) have the possibility to develop clubfoot as well.
- Maternal smoking during pregnancy
- Too little of amniotic fluid during pregnancy. The baby may increased the risk of clubfoot.
Complications
Clubfoot may cause the child have difficulty in walking if left untreated. Some challenges to consider are as follows:
- Movement. The flexibility of the foot is quite limited
- Leg length. The clubfoot leg may be quite shorter than the normal leg.
- Calf size. The foot and calf sizes will be slightly smaller
On the other hand, serious conditions might arise if it’s left untreated such as:
- Arthritis
- Poor self-image. This is mostly like to happen during the teenage years.
- Inability to walk normally. The affected foot will not be able to walk using its sole so other parts of the foot that reaches the ground will be utilized when walking.
- Other problems due to walking adjustments. Natural development of the calf will be affected and because the foot is using its other parts when walking, the gait will be affected.
Diagnosis
Clubfoot can be determined during pregnancy starting at 20 weeks of pregnancy through ultrasound. It can also be observed instantly by the doctor during birth. Further investigation can be done by performing X-ray to the baby’s clubfoot to measure the severity of the condition.
Treatment
Treatment can start in the first 2 weeks after birth because a newborn baby has a very flexible joints, tendons and bones. The following treatments can be done:
- Manipulation and casting (Ponseti method). Most common treatment for clubfoot. Gentle stretching and manipulation of the affected foot followed by a long-leg cast to hold the foot in place. The process of stretching, re-positioning, and casting is repeated weekly until the foot is improved. Mostly the treatment takes about 6 to 8 weeks.
- Percutaneous Achilles tenotomy. A minor surgery usually done after manipulation and casting process, which can be performed to release the tightness in the Achilles tendon. After the procedure, a new cast will be applied to the leg for 3 weeks. The tendon will regrown to a proper, longer length.
It is better for the child to undergo treatment in order to improve the physical appearance of the foot, ability to walk and avoid any other disabilities in the future.
When the clubfoot of the child has been realigned, the following techniques shall be followed:
- Stretching exercises
- Special braces or shoes for the baby (also known as boots and bar). Should be recommended and supervised by the doctor, and worn constantly for as long as three months. After that, it can be worn while sleeping for up to three years. This method can fail if not done properly.
- French method (also called functional or physical therapy method). A non-surgical method combining Stretching, mobilization and taping done under the supervision of a physical therapist.
Surgery
A more invasive surgery may be needed if the condition persist even after the above treatments mentioned. The foot will be aligned and lengthened by the orthopedic surgeon. The baby will be in a cast for up to two months post-surgery. Then, braces should be worn to avoid the recurrence of clubfoot. Keep in mind that clubfoot may not be fully corrected but children who were treated early can live a full and active life.