Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Overview
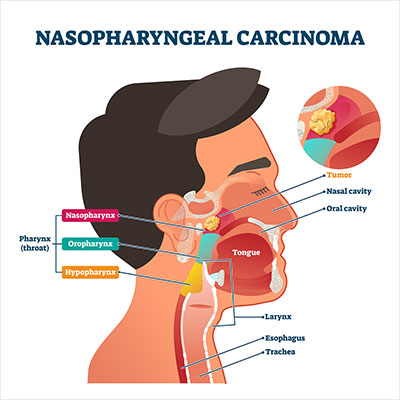
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma is a type of cancer that affects the nasopharynx. The nasopharynx is located between the back of your mouth and the back of your nose.
Asia, North Africa, and the Middle East are among the regions of the world where nasopharyngeal cancer is more common. The illness can affect people of any age, including children. The condition affects almost half of the people under the age of 55.
Despite the fact that this type of cancer often starts in the nasopharynx, it can also spread to other parts of the body. Early detection of nasopharyngeal cancer is challenging due to the symptoms being similar to those of other illnesses.
Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of the two are typically used to treat nasopharyngeal cancer. Consultation with the specialist is needed to determine the best course of action for treatment.
Symptoms
The following symptoms may appear in the later stages:
- Swollen lymph node which causes a mass in the neck
- Presence of blood in the saliva
- Presence of blood in nasal discharge
- Nasal congestion
- Ringing in the ears(tinnitus), frequent ear infection, ear fullness.
- Hearing loss
- Sore throat
- Pain and numbness of the face
- Having problems opening the mouth
- Speaking or breathing difficulty
- Headaches
If you notice these unusual signs and symptoms of nasopharyngeal cancer, consult your doctor immediately.
Causes
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma starts at the squamous cell lining of the nasopharynx. Generally, cancer begins when the normal cell undergo a genetic mutation which instructs the cells to grow and divide rapidly. This uncontrollable growth will continue to spread to other areas of the body (metastasis). The specific cause of nasopharyngeal carcinoma is unknown but Epstein-Barr virus may increase the risk of this disease.
Risk Factors
Some risk factors that may cause nasopharyngeal carcinoma are the following:
- Gender. Men are more likely to develop nasopharyngeal carcinoma than women.
- Race. People living in Southeast Asia, Southern China and Northern Africa and those of Asian descent.
- Age. Most commonly diagnosed in adults from 30 to 50 years old.
- Salt-cured foods. Salt-cured foods emit chemicals that may be inhaled and reach the nasal cavity.
- Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV). This virus is the most common cause of infectious mononucleosis. EBV infection can increase the chance of developing nasopharyngeal cancer.
- Family history of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
- Tobacco and alcohol. Excessive smoking of tobacco and alcohol consumption can increase the risk of developing nasopharyngeal cancer.
Diagnosis
- Physical exam. The doctor will perform a physical assessment, symptom analysis and palpate the neck to check for any swollen lymph nodes.
- Nasal endoscopy. A small, flexible tube with a camera is inserted inside the nasal cavity using local anesthesia to look for the abnormalities if the doctor suspects nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
- Biopsy. A small sample of suspected cancer tissue is removed using an endoscope or other instruments for examination under a microscope in the laboratory to look for any cancerous cells.
Tests to determine the extent of the cancer
The doctor will stage the cancer using these tests:
- X-ray
- Computerized Tomography (CT) Scan
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
- Epstein-Barr virus DNA levels test
After the doctor has checked the extent of cancer, it will be staged by using Roman numerals from I to IV. The lower stages means that the cancer is localized within the nasopharynx, while stage IV means that the cancer is in its advanced stage and has spread to other parts of the body. Staging will help find out which treatment is appropriate and monitors the prognosis of the disease.
Treatment
The treatment of choice is based on the cancer stage, the patient’s general health and the patient’s own decision of treatment options.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses strong energy beams through X-rays or protons to fight cancer cells. The most common radiation therapy approach for nasopharyngeal cancer is called external beam radiation, which focuses radiation directly on the area where the cancer is, using a machine that is navigated over the patient’s body while the patient is lying on the table. This can be used for smaller tumors or can be combined with chemotherapy.
In certain cases, internal radiotherapy (also called brachytherapy) may be needed if nasopharyngeal cancer was recurrent after initial treatment. Radioactive seeds or wires are implanted in the tumor or near the tumor.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is administered orally or intravenously to destroy cancer cells. There are 3 types of chemotherapy to treat nasopharyngeal carcinoma:
- Chemoradiation or concomitant therapy. Chemotherapy given at the same time as radiation therapy. This is used to strengthen the effect of radiation therapy, but the side effects of both are more potent and less tolerable for the patient.
- Chemotherapy after radiation therapy. Chemotherapy may be applied after radiation therapy to kill the remaining cancer cells or those that have spread.
- Chemotherapy before radiation therapy (Neoadjuvant chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is done before radiation or concomitant therapy. Although further research has to be done to prove the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Surgery
Surgery is not a common treatment for nasopharyngeal cancer but may be used to remove cancerous lymph nodes in the neck. Sometimes, the doctor removes a nasopharyngeal tumor by reaching this area through the roof of the mouth to access the area to remove the cancer.




