Overview
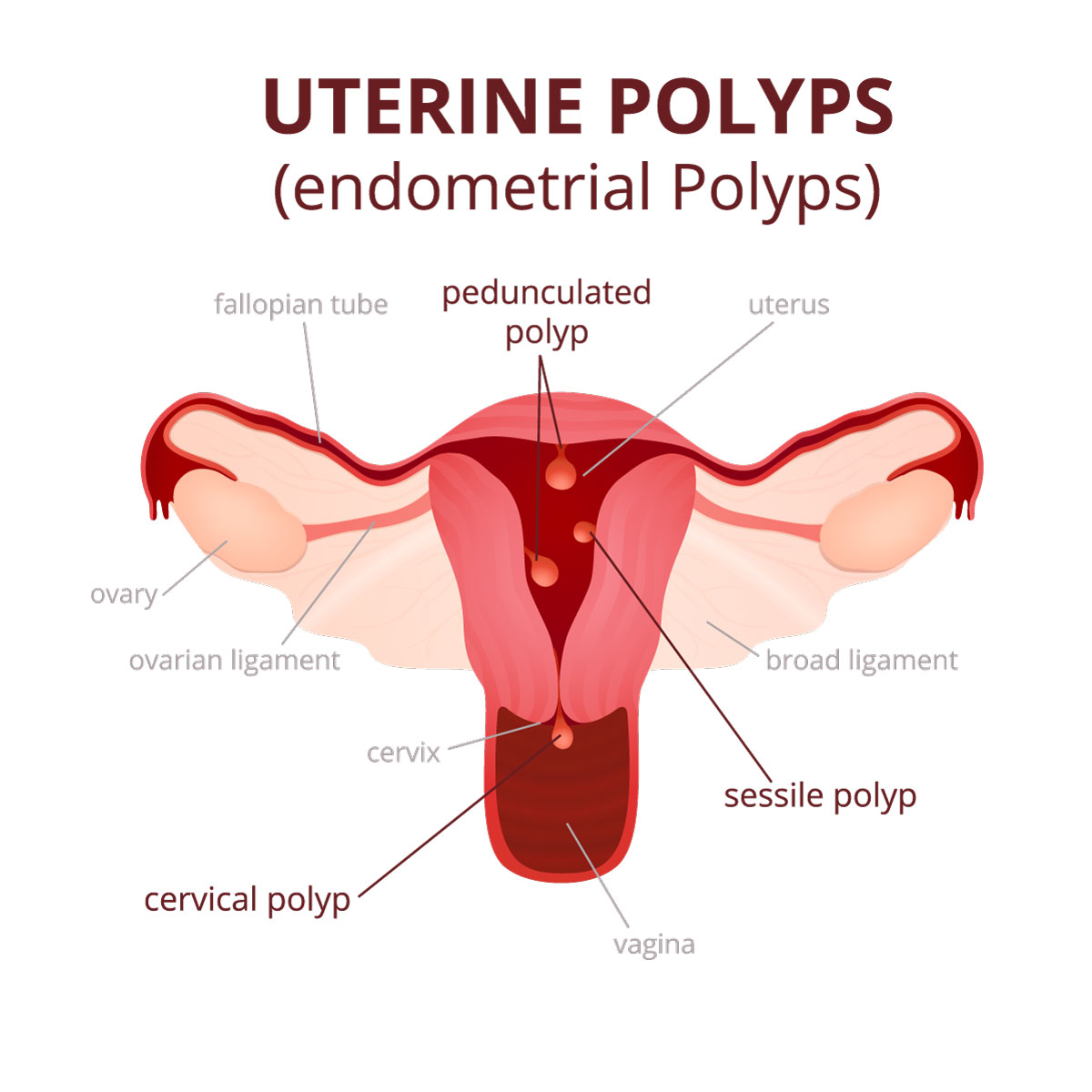
Uterine polyps, also called endometrial polyps, are abnormal growths on the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium) that extend into the uterine cavity. Most uterine polyps are noncancerous (benign). However, they can sometimes become cancerous (precancerous polyp). Uterine polyps can be found on the uterine walls, connected by a small stalk or a huge base. They vary in size from a few millimeters to a few centimeters.
Uterine polyps can be found as a single or multiple masses and they can be local in the uterus or go down to the cervix, and to the vagina. They are usually found in women in their menopausal stage, but even younger women can have them as well.
Treatment options for uterine polyps could include observation, medication, and surgical removal.
Symptoms
Uterine polyps have the following signs and symptoms:
- Irregular menstruation
- Postmenopausal vaginal bleeding
- Bleeding between menstruations
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Infertility
If you notice any of these symptoms, consult your doctor immediately. In some women, these symptoms can be mild or non-existent with occasional light spotting or bleeding.
What Causes Vaginal Polyps?
The cause of uterine polyps is unknown. However, hormonal factors are found to play an important role in developing the polyps. Uterine polyps most likely develop from an imbalance of the hormone estrogen.
Risk Factors
The risk factors for uterine polyp formation include:
- During menopausal or after menopausal period
- Tamoxifen medication intake (used for breast cancer treatment)
- Hypertension
- Obesity
Diagnosis
These tests may be performed if you are suspected to have uterine polyps:
-
- Pelvic examination: An examination of the genitals will be done. Index and middle finger will be inserted into the vagina while pressing the other hand on the abdomen to palpate the uterus and ovaries. A speculum device will be inserted to examine the vagina to look for any abnormalities of the cervix and vagina.
- Transvaginal ultrasound. A thin tube equipment is inserted into the vagina and uses sound waves to view images of the uterus and its interior. The polyp can either be seen clearly or viewed as a thick tissue of the endometrium.
Another procedure linked to transvaginal ultrasound is called hysterosonography or also known as sonohysterography. It injects saline into the uterus using a tiny tube inserted through the vagina and cervix. The saline inflates the uterine cavity making it easier to be seen during the ultrasound. - Hysteroscopy. A procedure done by inserting a thin, flexible tube with a light into the uterus through the vagina and cervix. Doctor can inspect the cavity inside of the uterus and endometrium.
- Endometrial biopsy. A procedure done by inserting a thin, flexible tube through the cervix to remove of a tissue sample from inside the uterus. Once the samples have been collected, they will be sent to the laboratory for analysis. This involves removing tissue from your uterus lining for laboratory analysis. Biopsy can detect uterine polyps.
Uterine polyps are usually benign but some uterine polyps can appear to be precancerous types of abnormalities, such as endometrial hyperplasia or uterine cancers, known as endometrial carcinomas. The doctor usually suggests polyp removal and sends the sample tissue to be analyzed in the laboratory for uterine cancer.
Treatment
The doctor will suggest the following treatment options for uterine polyps:
- Close observation. If the polyp is small and asymptomatic, they usually disappear on their own. It does not require treatment unless there is a risk of developing uterine cancer.
- Medication. Hormonal medication like progestin and gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist may provide temporary relief from the symptoms of uterine polyp.
- Surgical removal. An instrument is inserted into a device called a hysteroscope to reach the uterus and remove the polyp. The polyp is then sent to the laboratory for analysis.
If uterine polyp contains cancerous cells, the doctor will discuss the treatment options of your cancer.




