Coarctation of the aorta
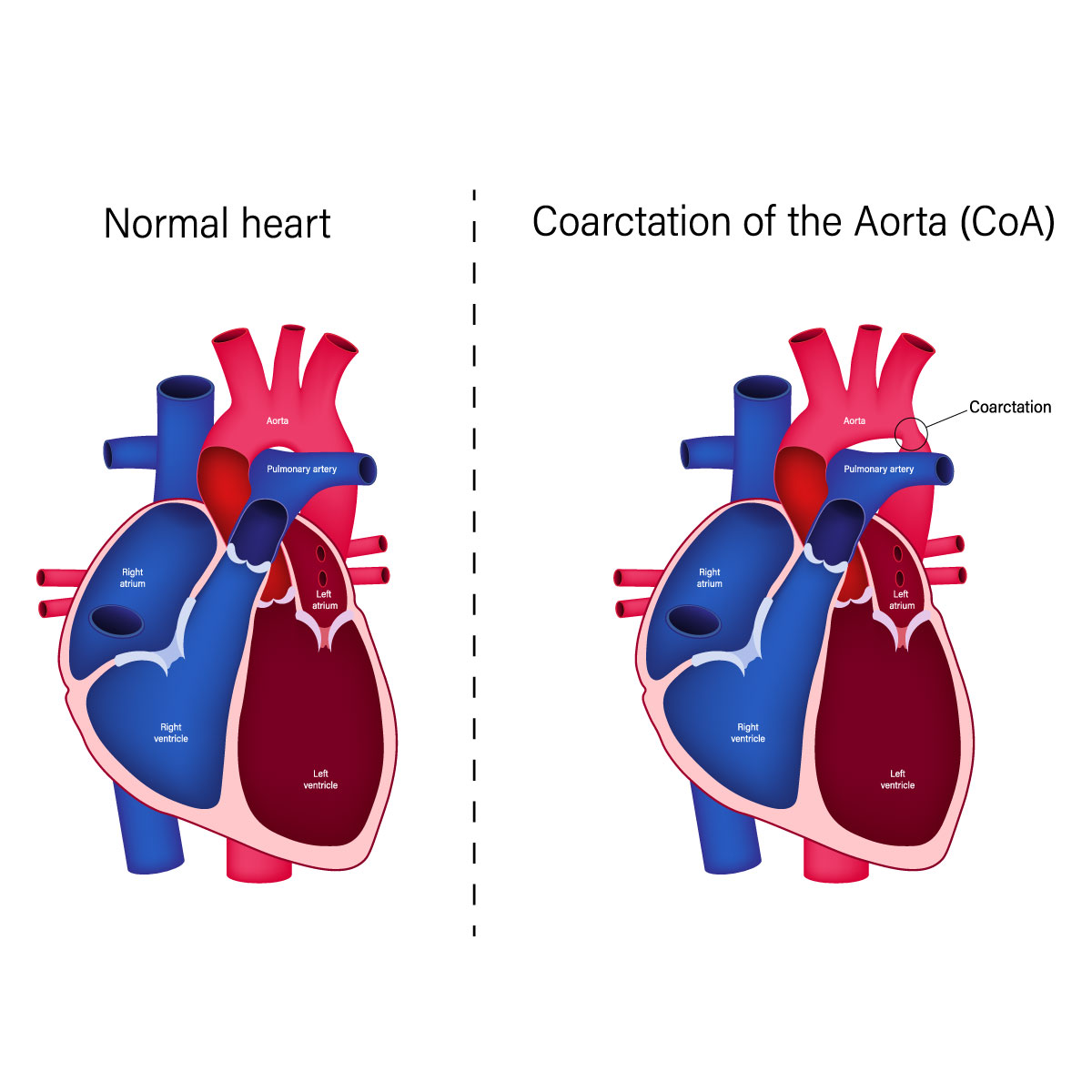
Overview
Aortic coarctation is a hereditary heart disease which usually occurs with other congenital heart defects. If aortic coarctation, or the narrowing of the aorta, occurs, the heart must work harder to pump blood through the artery because the aorta is the largest artery responsible for moving oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the entire body. The symptoms vary from mild to severe and it may be undetectable until the person gets older. Aortic coarctation patients are recommended to see a doctor for treatment as the success rate is high if treatment is received on time.
However, most patients must do thorough follow-up for the rest of their life to monitor the symptoms.
Symptoms
In most cases, aortic coarctation does not cause any symptoms. Mild coarctation can become detectable in adulthood. Symptoms can show up in newborns with severe aortic coarctation within a short period of time after birth.
The symptoms that can be found in those newborns with aortic coarctation include:
- Breathing difficulty
- Feeding difficulty
- Excessive sweating
- Recklessness
- Pale skin
After infancy period, the patients with aortic coarctation may experience the following symptoms:
- Chest pain
- Headache
- Hypertension
- Muscle spasm in the legs or feeling cold in the feet
- Weak muscles
- Nasal bleeding
The blood pressure depends on the area affected by the aortic coarctation. For example, the arms tend to have high blood pressure while the legs and ankles tend to have a lower one.
Other congenital heart conditions that happen together with aortic coarctation can cause any other symptoms too, depending on what the other illness is.
A child with any of the following symptoms is recommended to see a doctor:
- Severe chest pain
- Passing out
- Sudden difficulty breathing
- Hypertension without known causes
Causes
The cause of aortic coarctation is still not clear. As it is a congenital heart disease, it is mostly found since birth and barely develops after infancy.
However, the risk of developing aortic coarctation can be raised with any of the following factors:
- Severe trauma
- Atherosclerosis, or the thickening of the arteries
- Takayasu arteritis, of arterial inflammation
Although aortic coarctation can happen in any area of the aorta, the ductus arteriosus, or the blood vessel that connects the left pulmonary artery to the aorta, is at the most common location of the disease.
The wall of left ventricle is the highest risk of becoming thickened (hypertrophy). The reason for this is because once the aorta is narrowing, the left ventricle must pump blood harder through the narrowed aorta, causing the blood pressure in the chamber to be higher which causes its wall to thicken.
Risk factors
Genetic disorders and sex are among the risks of coarctation of the aorta. For example, having a genetic disease like Turner syndrome or being a male put one at a higher risk of developing this heart condition.
Aortic coarctation patients tend to have other congenital heart diseases too which puts them at higher risk. They include:
- Bicuspid aortic valve: a disorder where a patient has only two flaps (cusps) instead of three like normal people. The heart’s left ventricle is separated from the aorta with this aortic valve.
- Subaortic stenosis: This disease causes the area below the aortic valve to narrow, blocking the blood flow from left ventricle to aorta.
- Patent ductus arteriosus: This abnormality occurs when a newborn’s ductus arteriosus, or a blood vessel that connects the left lung artery to the aorta, remains open after childbirth. Usually, this blood vessel is open when the baby is still in the womb to let blood circulate around the lungs and will close right after the baby is born.
- Leaky wall between the left and right sides of the heart: This disorder causes the mixing of oxygen-rich blood from the left side of the heart and oxygen-poor blood in the right side of the heart. The disease is called atrial septal defect if the hole is in the heart wall between the upper chambers and called ventricular septal defect if the hole is in the lower chambers.
- Congenital mitral valve stenosis: causes the mitral valve, which is located between the upper and lower left heart chambers, to narrow and obstructs blood flow in the left side of the heart. Symptoms such as panting and difficult breathing especially when exercising or lying down are most common.
Diagnosis
Severe aortic coarctation may be detected while the baby is still in the womb with ultrasound or right after birth. How soon a doctor can detect aortic coarctation depends on how severe the disease is.
Mild aortic coarctation, on the other hand, is generally asymptomatic in adults and older children and does not affect their health.
A diagnosis of coarctation of the aorta is performed by looking for any of the following signs:
- High blood pressure in the arms
- The legs have a lower blood pressure than the one of the arms
- The legs have a weak or delayed pulse
- Heart murmur, or a whooshing sound
Coarctation of the aorta can be diagnosed with any of the following tests:
- Echocardiogram: This test helps to locate aortic coarctation and determine its severity to determine the necessary treatment. Sound waves are used to make moving images of the heart, which can help confirm if the heart has any other congenital conditions, such as a bicuspid aortic valve.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): In case of severe aortic coarctation, this test helps determine if the walls of the lower heart chambers are thickening, knows as ventricular hypertrophy. The test can be quickly completed without causing pain by measuring the electrical activity of the heart through sensors attached to the chest or the arms or legs and using wires to connect the sensors to a machine where the results appear or are printed out.
- Chest X-ray: Aortic coarctation can be determined with this procedure as it creates images of the heart and lungs, where the narrowed aorta at the area of the coarctation can be found.
- Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): This test is useful for helping the medical team make a treatment plan as it creates detailed images of the heart and blood vessels by using magnetic fields and radio waves making it easier to locate which area of the aorta is narrowing, assess its severity, see if any other blood vessels have been injured with the disease as well as find other heart disorders.
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan: This test shows detailed cross-sectional images of the body by using X-rays.
- CT angiogram: With a dye and special X-rays, the test is useful for planning for treatment, locating the disease and measuring its severity level as it shows blood flowing in the veins and arteries as well as affected blood vessels.
- Cardiac catheterization: The test helps to assess how severe the blockages in the heart arteries are by inserting a thin and flexible tube into a blood vessel in the groin or wrist before guiding the tube to the heart. The surgeon then injects dye through the catheter which flows to arteries of the heart to allowing to see the vessels more easily on X-ray images or video. Sometimes a doctor also uses this catheterization process to treat coarctation of the aorta.
Treatment
Coarctation of the aorta can be treated in many ways, such as medications to keep the conditions in control and surgery to get the aorta fixed. A cardiovascular surgeon or a cardiologist will choose the best treatment for you based on your age of the time the disease is found and the severity of the disease.
In certain cases, the medical team will treat aortic coarctation together with other congenital heart issues if they have found any of them in your body.
Medication
Your doctor might prescribe blood pressure medications before surgery to repair the aorta to enhance the efficiency of the surgery. You might be prescribed blood pressure medications before or after repair surgery. Even in case of a successful surgery which helps normalize your blood pressure, you might still need to take the medications after the surgery.
In case of treating a baby with severe aortic coarctation, a doctor might prescribe a medication that keeps its ductus arteriosus open so that blood can flow through a narrowing area of the aorta until surgery is done.
Surgery
Aortic coarctation can be treated as following:
- Balloon angioplasty and stenting: This procedure is usually chosen first and it uses a thin and flexible catheter with an uninflated balloon inserted into an artery in the groin. The doctor will then use X-rays to guide the catheter through the blood vessels to the heart and then to the area affected by aortic coarctation. The doctor will inflate the balloon at the catheter to widen the aorta to allow blood to flow through the artery. The doctor might also try to prevent
aortic re-narrowing by placing a stent in the affected area to keep the artery open. - Resection with end-to-end anastomosis: In this procedure, the doctor tries to remove the narrowed area of the aorta (resection) before connecting the two normal parts of the aorta (anastomosis).
- Subclavian flap aortoplasty: A doctor tries to widen the narrowed part of the aorta using a part of the left subclavian artery, which is responsible for delivering blood to the left arm.
- Bypass graft repair: the surgeon changes the direction of blood in the area and the aorta affected by aortic coarctation by using a graft.
- Patch aortoplasty: This option is recommended for those whose coarctation affects a long area of the aorta. The surgeon will try to expand the affected area by cutting across the vessel to attach a synthetic material there.




