Sex headaches
Diagnosis
It’s likely that your doctor may advise:
Brain imaging
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). A magnetic field and radio waves are employed during the MRI test to provide cross-sectional images of the brain’s structure. A MRI can assist in identifying any underlying reasons why you are experiencing headaches.
- Computerized tomography (CT). CT creates cross-sectional images of the brain using an X-ray machine that revolves around the body. A CT scan of the brain may be performed in certain circumstances, particularly if your headache started fewer than 48 to 72 hours prior.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) and Computerized Tomography (CT) angiography. These examinations show the blood vessels inside the brain and neck as well as those going to them.
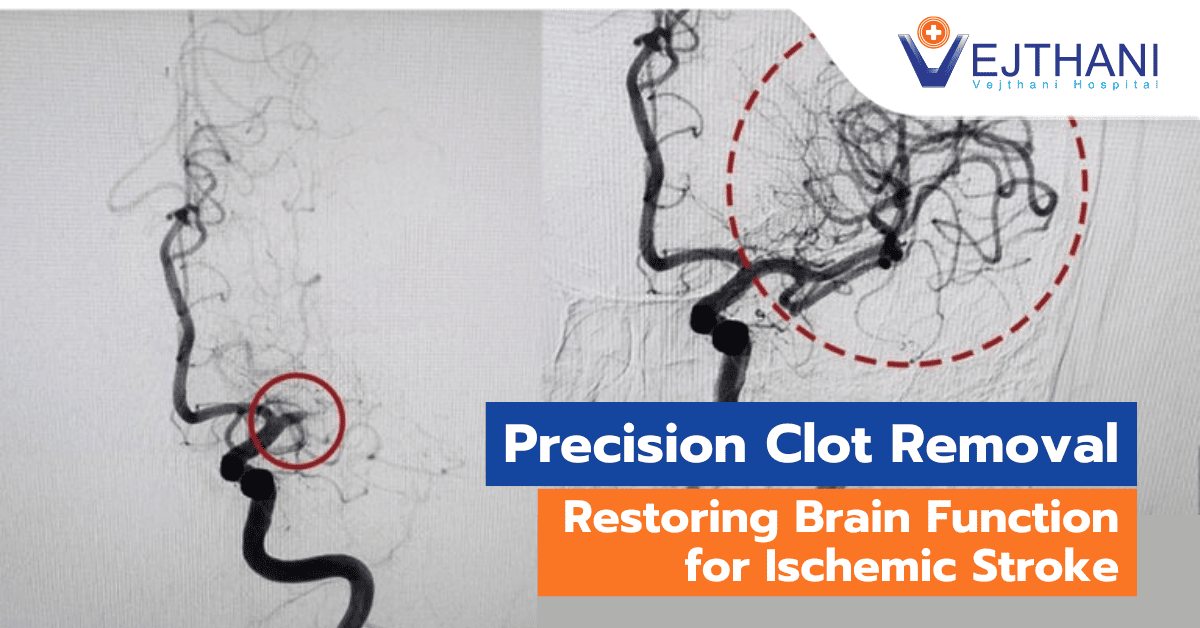
Angiograms
Your healthcare provider might suggest a cerebral angiogram, a diagnostic test that helps visualize the arteries in the neck and brain. In this procedure, a thin, flexible catheter is inserted into a blood vessel, usually starting from the groin area, and is guided up to an artery in the neck. A contrast agent is then administered through the catheter, enabling an X-ray device to produce precise images of the arteries in the neck and brain.
Spinal tap
In some cases, particularly if the headache started suddenly and brain imaging shows no abnormalities, a spinal tap (lumbar puncture) might be required. During this procedure, a healthcare provider removes a small sample of cerebrospinal fluid—the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. Analyzing this fluid can help identify any signs of bleeding or infection.
Treatment
In some instances, your first sex headache may also be your last. Some sex headaches improve rapidly, with the pain subsiding before any pain reliever can take effect.
Preventive medications
If you have a history of sex headaches and there’s no underlying condition, your doctor might suggest that you regularly take preventive medications. Options could include:
- Daily prevention medications. Medications like beta blockers such as propranolol or metoprolol are recommended, especially for those experiencing frequent or prolonged attacks. These medications, commonly used for high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, and migraines, may help. Calcium channel blockers like verapamil hydrochloride, also used for high blood pressure, could be considered as well, particularly for individuals with a history of migraine. Other migraine preventive medications may also be used in such cases.
- Occasional prevention medications. Indomethacin, an anti-inflammatory drug, or a triptan, which is used for migraine relief, can be taken about an hour before sexual activity to help prevent headaches.